Imidazoline: Your Solution to Corrosion Challenges, Emulsion Formation, Water & Fuel Treatment
Imidazoline-based inhibitors stand at the forefront of innovation in addressing corrosion, emulsification, and flocculation within the oil and petrochemical industries. These thermally stable, organic, nitrogenous bases form the foundational elements of this cutting-edge solution. Harnessing the power of imidazoline chemistry, these inhibitors are not merely chemicals; they represent a crucial leap in the development of film-forming organic corrosion inhibitors, playing a pivotal role across a myriad of industrial applications worldwide.
Their unique capability to establish a protective adsorption film on metal surfaces markedly reduces ion diffusion, effectively curtailing metal corrosion. This characteristic is especially beneficial in acidic and aggressive environments where the battle against corrosion is most fierce.
This 'Imidazoline' chemistry is the basis for one of the dominating types of film-forming organic corrosion inhibitors in oil and gas installations globally.
With their ability to form a protective adsorption film on metal surfaces, the Chemtex 901 Series effectively slows down ion diffusion, thereby significantly inhibiting metal corrosion. This makes them an indispensable ally in acidic and aggressive environments where corrosion poses a relentless threat.
This series meets extreme corrosion challenges for low and middle-range temperature oil and gas extraction sites, downhole operations. Depending on the conditions, operating limitations, and specific applications, and can be formulated as oil-soluble, oil-soluble/water-dispersible, or water-soluble/oil-dispersible.
Benefitsof Using Imidazoline
- API for corrosion inhibitor formulations
- High active matter content
- Good lubricity improver
- Thermally stable
- Soluble in both non-polar solvents and mineral oils
- Strongly cationic in acidic medium, adsorbing onto metal surfaces
- Hydrophobic; Water repelling agent
- Easy to handle, clear liquid at room temperature
- Excellent sour corrosion inhibition performance for low salinity brines and moderate temperature
- Good wetting agent
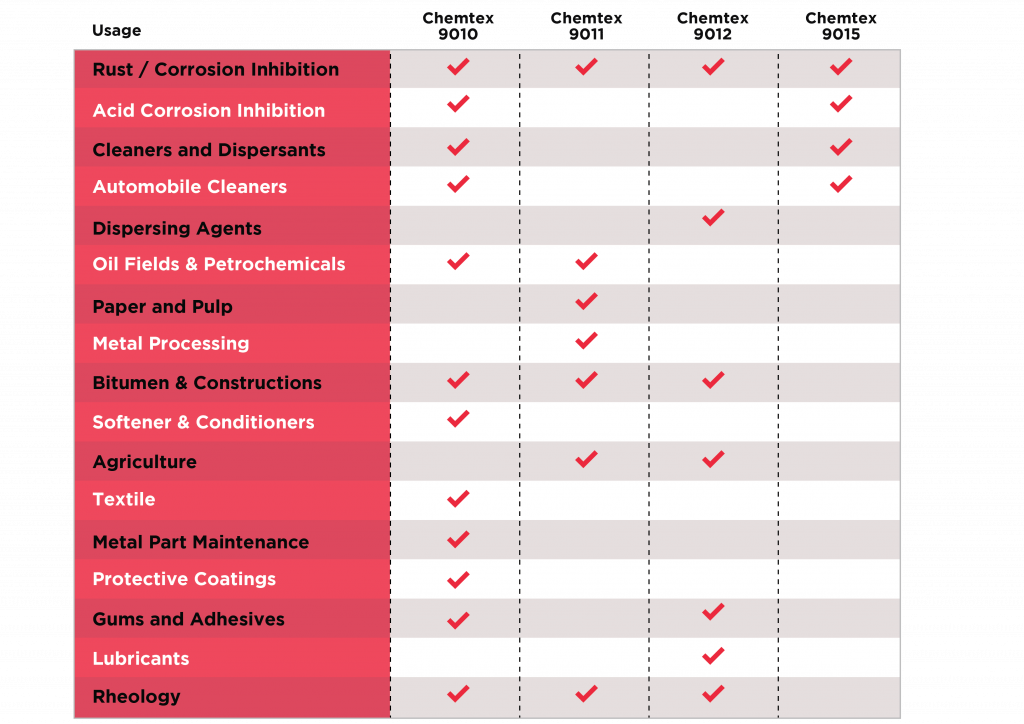
Application Areas for Imidazoline
-
Oil & Petrochemicals
API (Active Product Ingredient) for corrosion inhibitors abled to withstand water induced breakdown and acid corrosion
-
Acid Corrosion Inhibitor
Acid cleaning and metal pickling applications
-
Metal Surface Treatment
Excellent metal cleaning abilities with in combination with phosphoric acid, kerosene, antiscalant and corrosion inhibitors
-
Thickeners & Flocculants
Precipitate negative charged silicates, nitrates, borates
-
Paint & Adhesives
Improves adhesion and stickiness with water proofing abilities to paint
-
Textiles, Paper, Latex, Cement, Polymerization Reactions
Imidazolines act as emulsion stabilizers, lubricity improvers, and viscosifier, making metals resistant to corrosion
-
Car Wash Formulation
Oil/solvent based rinse aid concentrates preparation
-
Biocide
Help in formulating Pentachlorophenol which prevents microbial contamination
-
Laundry
Adds softness and resiliency to fabrics, inhibiting static buildup
-
Medical & Pharma
Broad spectrum antimicrobial, anti allergic, anti inflammatory properties
Applications Summarized
The Science Behind Imidazoline Corrosion Inhibition
Imidazoline adherents to heterocyclic group of compounds which has five membered rings with two nitrogen atoms.
Classified into two groups, Cationic & Amphoteric Imidazolines, the former is the Ammonium Mono Quaternary Salts with asymmetrical structure determined by cations, optically functioning in the aqueous solution where ionized.
The most widely used representative of this group is the tallow alkyl derivative. The unsaturated C18 consists of one double bond in a CIS isomer configuration which helps in lowering its melting point and is the sole reason behind its liquid state at room temperature. The saturated C18 has no double bonds, providing rigidity to the molecule and raising the melting point with reduced flow ability.
The nitrogen atom in the structure tends to provide some particular attributes like enhanced functional derivation, allowing the study of various functional group of Imidazoline radicals without effecting its paramagnetic properties. The head and the pendant group of the molecule helps in bonding of the same to surface while the hydrocarbon tail forms a protective layer or adsorptive layer.
Inhibition Mechanism:
The long hydrocarbon chain forms hydrophobic layers in solution that blocks any kind of reaction between the corrosive agent and the metal ions. The pendant side with an active functional group has nitrogen, oxygen and other heteroatoms, is responsible for chemical adsorption over the surface. The other Imidazoline derivatives act as cationic surfactants, determined by the nature of hydrocarbon or substituent groups attached to carbon or nitrogen atom of the heterocyclic ring.
